The observation of aerobic fermentation came as a big surprise. It is referred to as the crabtree effect in yeast.
Less efficient than the oxygen process aerobic fermentation creates acids in the cells that cause muscle fatigue and eventual failure.
What is aerobic fermentation. Aerobic fermentation or aerobic glycolysis is a metabolic process by which cells metabolize sugars via fermentation in the presence of oxygen and occurs through the repression of normal respiratory metabolism. It is referred to as the crabtree effect in yeast. And is part of the warburg effect in tumor cells.
Aerobic fermentation occurs when the cells demand more energy than can be produced from an oxygen reaction. Part of the cellular reaction still occurs and some atp is formed. Less efficient than the oxygen process aerobic fermentation creates acids in the cells that cause muscle fatigue and eventual failure.
Aerobic fermentation occurs in the presence of oxygen. It usually occurs at the beginning of the fermentation process. Aerobic fermentation is usually a shorter and more intense process than anaerobic fermentation.
Oxygen limitation is a major problem in aerobic fermentations because oxygen has a low solubility in water. The observation of aerobic fermentation came as a big surprise. It was and it is considered an inefficient form of metabolism because fermentation has a lower atp yield than oxidative phosphorylation.
It was and it is considered a wasteful phenomenon because fermentation results in overflow metabolism. Aerobic fermentation is an energy production method. Anaerobic fermentation is a decomposition method.
Stages include glycolysis krebs cycle and electron transport system. Anaerobic fermentation has no glycolysis or other stages. Aerobic fermentation is a type of reaction that causes the production of energy by completely decomposing the food while anaerobic fermentation is the chemical process of biological compounds.
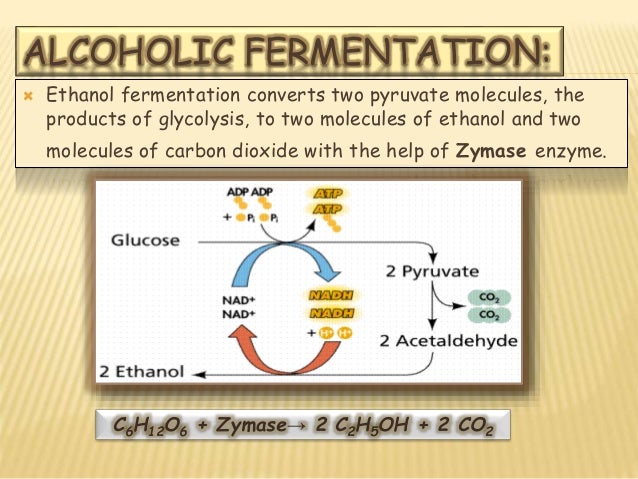
Aerobic fermentation occurs in the living organisms. On the flip side anaerobic fermentation occurs outside the living organisms body. Alcoholic fermentation is carried out by single celled organisms including yeasts and some bacteria.
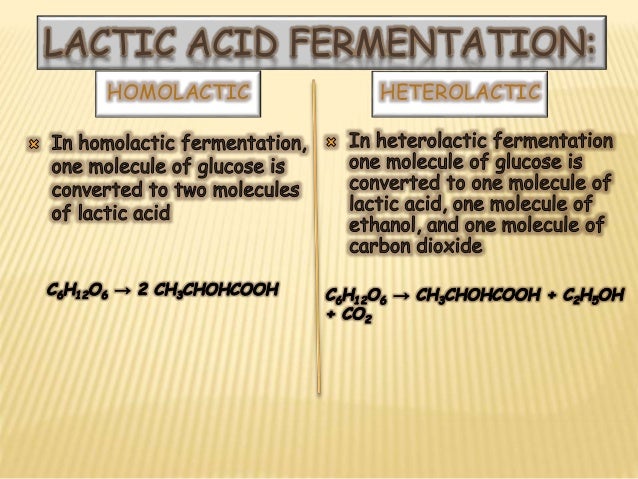
We use alcoholic fermentation in these organisms to make biofuels bread and wine. Lactic acid fermentation is undertaken by certain bacteria including the bacteria in yogurt and also by our muscle cells when they are worked hard and fast. Beyond lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation many other fermentation methods occur in prokaryotes all for the purpose of ensuring an adequate supply of nad for glycolysis table 2.
Without these pathways glycolysis would not occur and no atp would be harvested from the breakdown of glucose. Fermentation chemical process by which molecules such as glucose are broken down anaerobically. More broadly fermentation is the foaming that occurs during the manufacture of wine and beer a process at least 10 000 years old.
The frothing results from the evolution of carbon dioxide gas though this was not recognized until the 17th century. Anaerobic fermentation is a method cells use to extract energy from carbohydrates when oxygen or other electron acceptors are not available in the surrounding environment. This differentiates it from anaerobic respiration which doesn t use oxygen but does use electron accepting molecules that come from outside of the cell.